Файл: Fsbei he northWestern State Medical University named after I. I. Mechnikov Ministry of Healthcare of the Russian Federation.doc
ВУЗ: Не указан
Категория: Не указан
Дисциплина: Не указана
Добавлен: 28.03.2024
Просмотров: 63
Скачиваний: 0
ВНИМАНИЕ! Если данный файл нарушает Ваши авторские права, то обязательно сообщите нам.
ENDEMIC GOITER
а) occurs as a result of excess iodine in soil and water
b) characterized by hypofunction of the thyroid gland
c) occurs as a result of iodine deficiency in soil and water
d) characterized by hyperthyroidism
e) is a hereditary disease
Тest 7
CHOOSE ALL CORRECT ANSWERS:
The action of the hormone in the direct intracellular type of signal transmission is realized due to
а) protein synthesis induction
b) cascade signal amplification
c) allosteric regulation of enzyme activity
d) repression of protein synthesis
e) activation of enzymes by covalent modification
Тest 8
Match the exact correlation
ONE Question – ONE ANSWER
| Manifestation of action | Hormone synthesis and receptor status |
| 1) growth retardation in children 2) the dwarfism of Laron 3) pygmy dwarfism 4) gigantism 5) acromegaly | а) insufficient synthesis of growth hormone (GH) in childhood b) excessive synthesis of GH in childhood c) excessive synthesis of GH in adults g) defect of receptors for GH in the liver, synthesis of GR is normal d) a postreceptor defect in signal transmission, GH syntax is normal |
Тest 9
CHOOSE ALL CORRECT ANSWERS:
The action of the hormone in the mediated type of signal transmission is realized due to:
а) protein synthesis repression
b) cascade signal amplification
c) allosteric regulation of enzyme activity
d) induction of protein synthesis
e) activation of enzymes by covalent modification (phosphorylation)
Тest 10
CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER:
Clinical manifestations: in women amenorrhea, galactorrhea, gynecomastia, in men impotence and gynecomastia are characteristic of:
а) increased synthesis of growth hormone
b) increase the synthesis of luteinizing hormone
c) increased synthesis of prolactin
d) increased synthesis of follicle-stimulating hormone
e) increase the synthesis of sex hormones
Тest 11
CHOOSE ALL CORRECT ANSWERS:
| Hormone | Manifestation of action |
| lutenizing | a) progesterone production by the corpus luteum b) growth of ovarian follicles c) the growth of testis cells (Sertoli cells) d) production of androgens by Leydig cells of the testes e) production of estrogen by ovarian follicles |
Тest 12
CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER:
| Manifestation of action infertility or impotence, associated with impaired growth and maturation of germ cells | Снижение синтеза гормона a) progesterone b) lactogenic hormone c) follicle-stimulating hormone d) luteinizing e) chorionic gonadotropin |
Тest 13
CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER:
| Manifestation of action infertility or impotence associated with impaired stimulation of the synthesis of sex hormones | Decreased synthesis of the hormone а) progesterone b) lactogenic hormone c) follicle-stimulating hormone d) luteinizing e) chorionic gonadotropin |
Тest 14
CHOOSE ALL CORRECT ANSWERS:
The ovulation process is characterized by an increase in the level of:
а) progesterone
b) oxytocin
c) lactotropic hormone
d) follicle-stimulating hormone
e) luteinizing hormone
Тest 15
CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER
Hydrophobic signaling molecule:
а) penetrates the cell using a carrier
b) as a rule, does not penetrate into the cell
c) penetrates the cell by internalization
d) penetrates the cell without a carrier
e) penetrates the cell by active transport
Тest 16
CHOOSE ALL CORRECT ANSWERS:
| Hormone | Manifestation of action |
| follicle-stimulating | а) progesterone production by the corpus luteum b) growth of ovarian follicles c) the growth of testis cells (Sertoli cells) d) production of androgens by Leydig cells of the testes e) production of estrogen by ovarian follicles |
Тest 17
CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER:
Hydrophilic signaling molecule:
а) penetrates the cell using a carrier, interacts with the membrane receptor
b) as a rule, does not penetrate into the cell, interacts with the membrane receptor
c) penetrates into the cell without a carrier, interacts with the cytoplasmic or nuclear receptor
d) penetrates the cell by active transport, interacts with the cytoplasmic or nuclear receptor
e) penetrates the cell by facilitated diffusion, interacts with the cytoplasmic or nuclear receptor
Тest 18
CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER:
Adrenocorticotropin (ACTH):
а) is synthesized in the adrenal glands, is a hormone of protein nature
b) is synthesized in the adrenal glands, is a derivative of the tyrosine amino acid
c) is synthesized in the adrenal glands, is a steroid
d) is synthesized in the pituitary gland, is a hormone of protein nature
e) is synthesized in the pituitary gland, is a steroid
Тest 19
CHOOSE ALL CORRECT ANSWERS:
Signal molecules are:
a) hormones
b) biogenic amines
c) neurotransmitters
d) prostaglandins
e) end products of metabolic cycles
Тest 20
CHOOSE ALL CORRECT ANSWERS :
Luteinizing hormone
а) is synthesized by the sex glands, is necessary for the normal course of pregnancy
b) is synthesized by the pituitary gland, necessary for the ovulation process
c) is synthesized by the corpus luteum, is necessary for the normal course of pregnancy
d) is synthesized by the sex glands, determines the secondary sexual characteristics
e) is synthesized by the pituitary gland, stimulates the synthesis of sex hormones
Тest 21
CHOOSE ALL CORRECT ANSWERS:
To hormones of protein and peptide nature belong:
а) vasopressin
b) thyroxine
c) thyrocalcitonin
d) adrenaline
e) insulin
Тest 22
Match the correspondence:
One question may correlate with a few answers
| Type of reception | Action characteristic |
| 1) direct 2) membrane | а) requires secondary intermediaries b) does not require secondary intermediaries c) the hormone penetrates the cell d) the hormone does not penetrate the cell e) the response develops after 30-60 minutes f) the response develops after 8-12 hours |
Тest 23
CHOOSE ALL CORRECT ANSWERS:
The following hormones are derived from amino acids:
а) oxytocin
b) thyroxine
c) thyrocalcitonin
d) adrenaline
e) estradiol
Тest 24
CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER:
The action of the hormone in the direct, intracellular type of signal transmission:
a) requires a secondary mediator, and affects the genetic apparatus of the cell
b) does not require a secondary mediator, does not affect the genetic apparatus of the cell
c) does not require a secondary mediator, affects the genetic apparatus of the cell
d) requires a secondary mediator, does not affect the genetic apparatus of the cell
e) does not correspond to any proposed option
Тest 25
CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER:
The presence of an internalization mechanism for insulin explains:
а) the ability of insulin to enhance the penetration of glucose into the cell
b) activate hexokinase
c) actiating phosphodiesterase
d) change the rate of glycogen synthesis through the regulation of cAMP concentration
e) the penetration of the hormone into the cell
Тest 26
CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER :
Chorionic gonadotropin in urine is determined for diagnosis:
а) placental tumors
b) early diagnosis of pregnancy
c) the onset of ovulation
d) pregnancy disorders
e) the formation of fibromyoma
Тest 27
CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER:
Prostaglandins:
а) are formed in the endocrine glands and act remotely
b) are formed in the endocrine glands and have a local regulatory effect
c) are formed in many tissues and have a local regulatory effect
d) are formed in many tissues, enter the bloodstream and have a remote effect
e) are formed only in the prostate and have a regulatory effect
Тest 28
CHOOSE ALL CORRECT ANSWERS:
The receptors represented by tyrosine protein kinases are characteristic of:
а) insulin
b) adrenaline
c) cortisol
d) growth factors
e) prostaglandins
Тest 29
CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER:
Progesterone is synthesized:
а) in the adrenal cortex
b) in the corpus luteum
c) in the anterior pituitary gland
d) in the interstitial cells of Leydig
e) in the ovaries
Тest 30
CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER:
Prolactin is synthesized in:
а) adrenal cortex
b) yellow body
c) the anterior pituitary gland
d) mammary glands
e) ovaries
Keys for the section:
«The mechanism of action of hormones, pituitary and thyroid hormones»
| Тest 1 b,c,e Тest 2 e Тest 3 b,e Тest 4 c Тest 5 а,b,d Тest 6 b,c Тest 7 а,d Тest 8 1а,2d,3e,4b,5c Тest 9 b,c.e Тest 10 c Тest 11 А,D,E Тest 12 C Тest 13 D Тest 14 de Тest 15 d | Тest 16 b,C Тest 17 b Тest 18 d Тest 19 а,b,c,d Тest 20 B.E Тest 21 а,c,e Тest 22 1b,c,f 2а,d.e Тest 23 b,d Тest 24 c Тest 25 e Тest 26 b Тest 27 c Тest 28 а,d Тest 29 b Тest 30 c |
1.Topic : Regulation of carbohydrate metabolism. Quantification of blood glucose.
Venue: Chair of Biochemistry.
Duration: 180 minutes
2. Objectives: Consider the general mechanisms of regulation of carbohydrate metabolism at several levels. Assess methods for determining glucose in the blood. Master the glucose oxidase method for determining blood glucose .
3. Specific tasks
The student must know:
1. The presence of different levels of regulation of carbohydrate metabolism.
2. Metabolic regulation by the principle of negative feedback on the example of regulation of aerobic oxidation of glucose by the concentration of the final product - ATP.
3. Metabolic regulation by the type of phosphorylation of dephosphorylation depending on the concentration in the cell of a secondary messenger (cAMP) using the example of the breakdown and synthesis of glycogen.
4. Hormonal regulation of glucose metabolism depending on the functional state of the body.
5. The rate of glucose in the blood. Types of hypo- and hyperglycemia, types of glucosuria.
The student must be able to: Quantify blood glucose.
The student must have: knowledge to evaluate the results obtained by the laboratory and interpret the data
-
Motivation - a doctor needs to have knowledge about the mechanisms of regulation of carbohydrate metabolism, be able to use this knowledge in medical practice and when conducting experimental studies in studying the mechanisms of the influence of various factors on the body.
-
Assignment for self-study:
Students should study recommended literature using self-study questions.
Basic Literature
5.1. Revise the lecture material on the topic: "Regulation of carbohydrate metabolism."
5.2 Биохимия: Учебник/ Под ред. Е.С. Северина. –М.: ГЭОТАР-МЕД, 2003. -С. 545-549, 572-592. 2011. -С. 534- 549, 560-580.
5.3пользовать при подготовке учебник Березов Т.Т., Коровкин Б.Ф. "Биологическая химия" М., Медицина 1998 , с. 357-361, 267-280, 292-294.
5.4 Подготовиться к лабораторной работе по методическим пособиям: Учебно-методическое пособие к практическим занятиям по биологической химии, часть 2 Санкт-Петербург., 2013
Additional literature.
5.5 Мари Р., Греннер Д., Мейес П., Родуэлл В. «Биохимия человека» М., Мир, 1993. –С. 212-224.
5.6 Медицинские лаборатоные технологии. Под ред. А.Н.Карпищенко, в двух томах. - СПб:"Интермедика". – 1999. – 656 с.
5.7. Trinder P. Determination of glucose in blood using glucose oxidase with an alternative oxygen acceptor // Ann. clin. Biochem. -1969, -Vol. 6. –P. 24.
5.8. Долгов В.В., Аметов А.С., Щетникович К.А., Ройтман А.П., Демидова Т.Ю. Лабораторная диагностика обмена углеводов, сахарный диабет. Лахема, 2000, 63с.
6. Questions for self-study:
6.1. Levels of regulation of carbohydrate metabolism.
6.2. Metabolic regulation by the principle of negative feedback on the example of regulation of aerobic oxidation of glucose by ATP concentration.
6.3. Key stages and enzymes of regulation of aerobic glucose oxidation.
6.4. Metabolic regulation by the type of phosphorylation - dephosphorylation depending on the concentration in the cell of a secondary messenger (cAMP) using the breakdown and synthesis of glycogen as an example.
6.5. What is reciprocal regulation?
6.6. Ways of glucose entering the cell and ways of using glucose by the body.
6.7. The rate of glucose in the blood.
6.8. Hormonal regulation of blood glucose levels: the mechanism of action of insulin, glucagon, adrenaline, glucocorticoids, adrenocorticotropic hormone, growth hormone and thyroxine on carbohydrate metabolism.
6.9. What is hyperglycemia, its types.
6.10. What is hypoglycemia, its causes.
6.11. What is glucosuria, its types.
6.12. The renal threshold for glucose, its value, biological meaning
6.13. What structural features of glucose are based on its qualitative and quantitative determination.
Question card sample – see Test for this Section
QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF GLUCOSE IN BLOOD
Glucose is the main carbohydrate in human blood; its content in whole blood on an empty stomach is 3, 3-5.5 mmol / l; in fasting venous serum 3.4-6.1 mmol / l. Other carbohydrates, fructose, mannose, galactose, lactose and pentose, are found in much smaller or trace amounts. In the narrow sense of the word “blood sugar” is meant only glucose. The level of blood glucose is influenced by the intake of carbohydrates with food; mobilization of liver glycogen; gluconeogenesis; tissue glucose oxidation; synthesis of heteropolysaccharides, pentoses, amino acids, synthesis of glycogen and fat and tissues. Glucose, being one of the most important components of the blood, is almost evenly distributed between plasma and uniform elements with a slight excess of its concentration in the plasma. Since glucose belongs to aldohexoses, and the aldehyde group is easily oxidized, this is widely used in the determination of glucose. To determine blood glucose, many methods have been proposed, which can conditionally be divided into 3 groups:
1.Reducometric methods are based on the restoring properties of glucose (the Hagedorn-Jensen method; Folina; Folina-Wu and others). The disadvantage of these methods is that in essence they determine not only glucose, but also a number of other reducing substances (glutathione, ADP, uric acid, creatine, glucuronic acids, vitamin C), the presence of which can lead to the determination of not “pure glucose” ”, And“ apparent sugar ”[Medical ..., 1999]. This group of methods has low specificity and considerable laboriousness.
-
Colorimetric methods are based on color reactions of glucose with certain compounds, for example, sulfuric acid, picric acid, anthron, ortotoluidine. All aldoghexoses are determined by these methods, but since glucose is the main representative of aldohexoses, the results obtained are close to the true glucose content in the blood. The disadvantage of the methods is the high toxicity of the reagents used.
3. Enzymatic methods are the most specific and accurate methods for the quantitative determination of glucose, in particular, glucose oxidase method, which determines the content of "true glucose", equal to 3, 4-5.6 mmol / l [Trinder P., 1969; Dolgov V.V. et al., 19 ..., Medical ..., 1999]. The determination is carried out on an empty stomach to avoid food hyperglycemia.
In some cases, an express determination of blood glucose is required. For these purposes, biochemical analyzers are used - glucometers, which allow the determination of glucose within 2-3 minutes after blood sampling. The basis of the work of analyzers, as a rule, is the glucose oxidase method.
Laboratory work
Quantitative determination of blood glucose by glucose oxidase method
The principle of the method: Glucose oxidase specifically catalyzes the transfer of two hydrogen atoms from the first carbon atom of glucose to atmospheric oxygen. In the course of the reaction, hydrogen peroxide is formed in equimolar amounts, which is decomposed by the second enzyme, peroxidase, and the atomic oxygen released during the reaction oxidizes the phenol derivative with 4-aminophenazine added to the reaction mixture, which changes color. The color intensity is proportional to the glucose content [Trinder P., 1969].
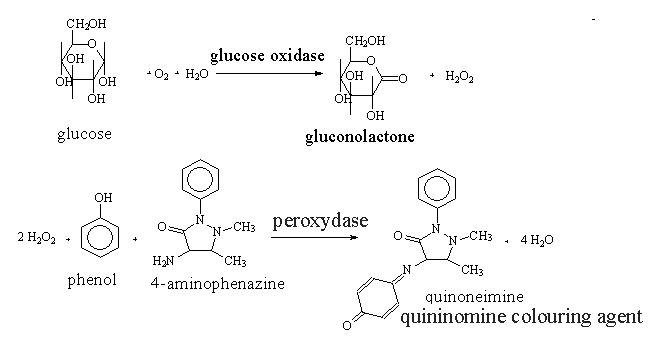
The course of work: in three tubes, 1` ml of glucose reagent is measured. 0.1 ml of a standard glucose solution (standard sample) is added to the first tube, 0.1 ml of blood serum to the second (test sample) and 0.1 ml of distilled water to the third (control). All samples are mixed and incubated for 15 minutes at a temperature of 37°C. Then measure the optical density of the sample and standard against the control solution. Blue filter 425-500 nm in ditches with a working distance of 10 mm.
Scheme for determining serum glucose
| Sample No. | Glucose Reagent (ml) | Standard Glucose solution (ml) | Test sample (ml) | Н2О (ml) | Optical density |
| 1 | 1 | 0,1 | - | - | Dст |
| 2 | 1 | - | 0,1 | - | D оп |
| 3 | 1 | - | - | 0,1 | - |
Calculations: Соп (mmol/l) = (Dоd/Dst) • 10
where Соп - glucose concentration in the test sample in mmol / l ;


