Файл: Учебное пособие по профессиональному иностранному языку для студентов 3 курса.docx
ВУЗ: Не указан
Категория: Не указан
Дисциплина: Не указана
Добавлен: 02.05.2024
Просмотров: 105
Скачиваний: 0
ВНИМАНИЕ! Если данный файл нарушает Ваши авторские права, то обязательно сообщите нам.
VOCABULARY
Task 1. Match the words in Column A with the correct definitions in Column B.
| A | B |
| 1. consumption | a) the act or process of buying, including any negotiations that this involves on price and availability. |
| 2. procurement | b) something that you buy. |
| 3. strive for | c) a plan that gives a list of events or tasks and the times at which each one should happen or be done. |
| 4. purchase | d) the process of buying or using goods, or the amount that people buy or use. |
| 5. schedule | e) to make a lot of effort to achieve something. |
| 6. customer | f) make smaller or less in amount, degree, or size. |
| 7. reduce | g) a person or company that buys goods or services. |
Task 2. Form nouns, verbs or adjectives from the following words.
| Noun | Verb | Adjective |
| 1. consumption | | |
| 2. purchase | | |
| | 3. reduce | |
| | | 4. strategic |
| 5. procurement | | |
Task 3. Match a line in A with a line in B to make word combinations as they are used in the Text B.
| A | B |
| 1. raw | a) benefits |
| 2. cost | b) agreements |
| 3. make | c) materials |
| 4. purchasing | d) orders |
| 5. take | e) schedule changes |
| 6. information | f) technology |
Task 4. Complete the sentences (1-5) with words from the box.
| experts cost customer reputation monitor |
1. Supply chain managers develop and …………. a company’s supply chain strategy.
2. Effective supply chain management systems minimize ………., waste and time in the production cycle.
3. The better and more effective a company’s supply chain management is, the better it protects its business …………… and long-term sustainability.
4. Supply chain management affects product and service quality, delivery, costs, …………….. experience and ultimately, profitability.
5. Modern supply chains take advantage of massive amounts of data generated by the chain process and are curated by analytical ……………. and data scientists.
LISTENING
Task 1. Watch the video about Supply Chain Management (SCM) and complete the sentences with words and phrases from the box.
(https://www.youtube.come/watch?v=R8rYsCmAEEY)
| costs raw materials services business landscape excess costs crucial elements capital requirements final products. |
1. Supply change is a connected network of individuals, organizations, resources, activities, and technologies involved in manufacturing and sale of products or ………………
2. Supply chain starts with the delivery of ……………… from a supplier to a manufacturer and ends with the delivery product or service to the end consumer.
3. Companies develop supply chains, so they can reduce their costs and remain competitive in a ………………... .
4. Supply chain management (SCM) is the management of the flow of goods and services and includes all processes that transform raw materials into ………….. .
5. By managing the supply chain, companies are able to cut ………… and deliver products to the consumer faster.
6. The supply chain manager tries to minimize shortages and keep…………….as low as possible.
7. Key performance indicators (KPIs) are ……………of a successful SCM strategy.
8. The time between paying for raw materials and receiving payment for goods delivered which matters in determining working ………………. .
Task 2. Watch the video about Supply Chain Management (SCM) again and discuss the following questions.
1. Why do companies develop supply chains?
2. What are the five parts of a supply management system?
3. What are the responsibilities of a supply chain manager?
4. What are key performance indicators (KPIs)? What is the importance of them?
SPEAKING
Task 1. Complete the short conversation with words in the box.
| calling speaking delivery date very much help |
Mr. Jones and Tim Hans are talking on the phone.
Mr. Jones: Hello! This is Peter Jones ………………..
Tim: Hello Mr. Jones. This is Tim Hans from Great Tech Corporation.
Mr. Jones: Oh, hello, Tim. How can I …………….you?
Tim: I’m calling to change the …………….of office supplies from September 10 to September 12.
Mr. Jones: OK, I’ve got it. No problem.
Tim: Thank you ………………
Mr. Jones: Thank’s for ……………. Goodbye.
Tim: Goodbye.
Task 2. Work in pairs. Act out the telephone conversation between two managers.
Student A: You are the manager. Make a call to speak to Mr. Jim Mars and ask for information about warehousing costs.
Student B: You are the manager. Say that your company is ready to give some discounts.
Task 3. Work in groups of 3-4 students. Discuss the differences between logistics and supply chain management. Choose one of the following topics.
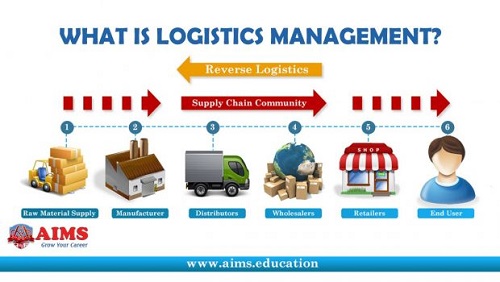
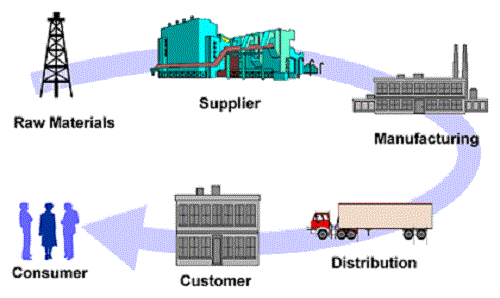
Group 1: How logistics and supply chain management are different.
Group 2: Technology for logistics and supply chain management.

USEFUL LANGUAGE
Presenting arguments
- Most importantly, I want to mention that...
- The primary argument for... is...
- Two/three... important arguments support my point of view...
- It's true/obvious/evident that ... However, ...
- While you might say that ...,
- It's important to remember that ...
- I agree with you that ... On the other hand, ...
- Although/even though it is true that... I believe that...
GRAMMAR REVIEW: Gerunds and infinitives
| Gerunds | Infinitives |
| 1. A gerund is formed by adding ‘ing’ to the base form of the verb. Gerunds can be used as the subject, subject complement, or the object in sentences. For example, - Starting a business requires a lot of work, time and money. (Gerund phrase as a subject) -Do you enjoy working in retail? (Object) - The project managers are happy about doing this project work. (Gerund phrase as an object of a preposition) Something that I hate is working long hours. (Gerund as a subject complement) | 1. The infinitive is when we use to + the base infinitive form of the verb. For example, I want to call them. |
| 2. Gerunds are also considered as a type of noun formed from a verb. For example, We enjoy reading a book. (Gerund) | 2. a) The simple infinitive refers to the same time as that of the preceding verb. For example, I was glad to see her. He must be very happy. b) The continuous infinitive refers to the same time as that of the preceding verb and expresses an action in progress or happening over a period of time. For example, I’m glad to be sitting here. You must be joking. c) The perfect infinitive refers to a time before that of the preceding verb. For example, I’m glad to have studied at the school. |
| 3. Some verbs that can be followed by gerunds are: admit advise anticipate appreciate avoid can’t help can’t stand consider delay deny dislike discuss enjoy finish mention mind miss postpone practice quit recall recommend regret report resent resist resume risk suggest tolerate try understand For example, She avoided telling them about her plans. | Some of the verbs can be followed by the ‘to+infinitive”: agree to do aim to do can’t afford to do can’t wait to do choose to do claim to do decide to do expect to do fail to do happen to do hope to do intend to do manage to do offer to do plan to do pretend to do refuse to do seem to do wish to do |
| 4. Verb+Preposition_Gerund: adapt to; accuse to; apologize for; approve of; argue about/against; ask about; believe in; blame for; care about; concentrate on; complain about; consist of; decide on; depend on; disapprove of; discourage from; engage in; forgive for; get used to; give up; help with; inquire about; insist on; interfere with; keep on; look forward to; object to; participate in; persist in; plan on; profit from; prepare for; prohibit from; put off; succeed in; suffer from; talk about; take part in; think about; warn about; work on; worry about. For example, She was accused of embezzling the organization’s funds. We would like to apologize for treating you this way. She complained about overpricing. | |
Note: Some verbs can be followed by the gerund or the infinitive form without a big change in meaning.
For example.
She started checking their order.
She started to check their order.
With other verbs, the meaning changes.
For example,
She has stopped smoking. (That means she no longer smokes.)
She stopped to rest for a few minutes. (That means she stopped what she was doing in order to rest.)
Task 1. Is the gerund in the following sentences used as a subject or as an object?
1. Being a new manager can be both thrilling and daunting with the pressure to perform well and lead a successful team.
a) subject
b) object
2. Developing a relationship with reporting employees is a key factor in managing.
a) subject
b) object
3. Knowing employees will make you a better manager, a manager who is more responsive to employee needs, moods, and life cycle events.
a) subject
b) object
4. Becoming a manager is a career shift just as much as deciding a profession you want to study in school.
a) subject
b) object
5. She hates going out at night.
a) subject
b) object
6. I don't mind working a lot.
a) subject
b) object
7. Managing compliance risk is all about ensuring that a business complies with all the relevant laws and regulations.
a) subject
b) object
8. Developing managerial skills is important for all professionals.
a) subject
b) object
9. They aren’t fond of reading e-books.
a) subject
b) object
Task 2. Put the verbs in brackets into the correct form (gerund or infinitive).
1. Managers fail ………… (create) standards and give people clear expectations, so they know what they are supposed to do, and wonder why they fail.
2. ……………..(enable) people to make decisions about their work is the heart of employee empowerment and the soul of employee engagement.
3. It's easy to want ……..(take) the new manager title and keep doing lots of the "fun" individual contributor tasks.
4. The models practiced ……… (walk) with a book balanced on their heads.
5. Mr.Edwards chose ………(accept) the management position in Chicago rather than the position in Miami.
6. Mrs. Naidoo appears……… (be) the most qualified person for the gob.
7. Frank offered ……….(help) us paint the house.
8. I demand ………(talk) to the manager of the hotel immediately.
9. She refused ………(speak) to me after our fight.
10. Ken decided on ………(go) going abroad next year.
11. We talked about ………….(go) to Italy for our summer vacations.
Task 3. Choose the most appropriate form (a-d) of the infinitive.
1. We expect him ……………… tomorrow.
a) to arrive
b) to be arriving
c) to arrive
d) to have arrived
2. We are ready ………………...
a) to be beginning
b) to be begun
c) to begin
d) to have begun
3. This report must …………… as soon as possible. It’s urgent!
a) be sent
b) have been sent
c) have sent
d) send
4. You should ……………… them an hour ago.
a) be called
b) call
c) have been called
d) have called
5. He is supposed to be writing a report now.
a) to write
b) to be writing
c) to have written
d) to writing
6. During this phase, team members complete the work that has been identified in the project plan in order …………… the goals of the project.
a) to reach
b) to have reached
c) to be reaching
d) reach
Task 4. Choose the correct gerund or infinitive from the parenthesis at the end of the sentence.
1. Sue remembers …………(buy) tomatoes at the supermarket because she usually takes a list. (buying/ to buy)
2. He stopped ………….(
read) the book at seven because it was time for dinner.(reading/ to read)
3. Sue definitely didn't forget …………..(ask) the teacher the question. (asking/ to ask)
4. John stopped ………..(make) a telephone call before he continued with his work. (making/ to make)
5. Have you ever forgotten ………….(get) a present for your friend’s birthday? (getting/ to get)
6. Sue stopped ………….(smoke) years ago because of the serious health problem. (drinking/ to drink)
7. I regret …………..(tell) my colleague that I am going out of business next month. (telling/ to tell)
