Файл: Учебное пособие по профессиональному иностранному языку для студентов 3 курса.docx
ВУЗ: Не указан
Категория: Не указан
Дисциплина: Не указана
Добавлен: 02.05.2024
Просмотров: 104
Скачиваний: 0
ВНИМАНИЕ! Если данный файл нарушает Ваши авторские права, то обязательно сообщите нам.
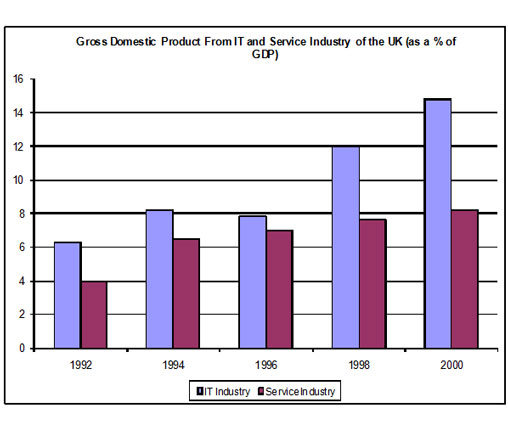
Gross Domestic Product in the UK
CASE STUDY 6:
T
 ask 1. Read the situation below and then prepare a strategic plan.
ask 1. Read the situation below and then prepare a strategic plan.Almaty Food Service, a successful medium-sized Kazakh manufacturer of dairy products and meat for the home and office, is interested in starting manufacturing subsidiaries in key overseas markets. To research potential locations in those markets, the company has organized a program of visits to regional business development groups which are interested in attracting foreign investors.
You are a manager for Almaty Food Service. This is a big step for your company to succeed in business. Do not forget that the choice of location might mean the difference between success and failure.
Take into consideration the following points:
a) Investigate the market place and learn how many foreign businesses are already located in the area.
b) Define supply of skilled labor.
c) Describe component manufacturers which are located nearby.
d) Analyze the conditions of the communications network.
Task 2. Prepare a presentation for the regional development business group about your company and its plans for expansion.
UNIT 7
LOGISTICS AND SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT
LEAD-IN
Task 1. Discuss the following questions.
1. What is logistics?
2. What is the role of logistics in an organization?
READING

Task 1. Discuss the following question before you read the text.
Which of these are duties and responsibilities of a logistics manager?
a) To manage warehouse inventory.
b) To recruit, interview, hire, and train new staff in the department.
c) To monitor and manage budgets.
d) To handle discipline in accordance with company policy.
e) To select carriers for transportation and negotiate rates and contracts with carrier.
f) To keep up-to-date on shipping carriers, routes and rates and any changes.
g) To design and implement a strategic business plan.
Text A.
Task 2. Read the text bellow and then discuss the following questions.
1. What does logistics refer to?
2. What does the complexity of a logistic operation depend on?
3. What does logistics management entail?
LOGISTICS
Logistics refers to the overall process of managing how resources are acquired, stored, and transported to their final destination. Logistics management involves identifying prospective distributors and suppliers and determining their effectiveness and accessibility. Logistics managers are referred to as logisticians.
"Logistics" was initially a military-based term used in reference to how military personnel obtained, stored, and moved equipment and supplies. The term is now used widely in the business sector, particularly by companies in the manufacturing sectors, to refer to how resources are handled and moved along the supply chain.
No business project could be completed without strong logistics support behind it. Even the smallest businesses have to find suppliers, which means they have to consider logistics. Of course, the complexity of a logistics operation generally depends on the number of firms involved, the nature of the supply chain and the distance. Larger businesses which specialize in a number of different areas will often have a more extensive logistics operation of their own.
The concept of business logistics has been transformed since the 1960s. The increasing intricacy of supplying companies with the materials and resources they need, along with the global expansion of supply chains, has led to a need for specialists known as supply chain logisticians.
Logistics is planning, execution, and control of the procurement, movement, and stationing of personnel, material, and other resources to achieve the objectives of a campaign, plan, project, or strategy. In other words logistics is the overall management of the way in which all kinds of resources are obtained, stored and moved to the locations where they are required. It may also be defined as the ‘management of inventory in motion and at rest’. Logistics management entails the following: to identify potential suppliers and distributors; to evaluate how accessible and effective they are; to establish relationships and to sign contracts with the companies who offer the best combination of price and service.
In the modern era, the technology boom and the complexity of logistics processes have spawned logistics management software and specialized logistics-focused firms that expedite the movement of resources along the supply chain. One reason large online retailers like Amazon have come to dominate the retail landscape is the overall innovation and efficiency of their logistics along every link of the supply chain.
(Adapted from https://www.terms/l/logistics.asp)
Task 3. Are the following statements (1-7) true, false or not given according to the Text A?
1. A professional working in the field of logistics management is called a logistician.
2. Logistics refers to the transport and storage of goods throughout the supply chain.
3. Even the smallest businesses have to find suppliers.
4. Larger businesses which specialize in a number of different areas will often have a less extensive logistics operation of their own.
5. The concept of business logistics has been transformed since the 1950s.
6. Logistics management is part of all the levels of planning and execution, including strategic, operational and tactical.
7. The technological development and the complexity of logistics processes have created logistics management software.
Task 4. Match the sentences beginnings (1-6) with the correct endings (a-f) to make a short summary of the Text A. Read the Text A again if necessary.
1. Logistics refers to the overall process of managing how resources ……………
2. Logistics managers are referred to …………………
3. “Logistics” is now used widely in the business sector, particularly by companies in the manufacturing sectors, to refer to ………………………
4. Even the smallest businesses have to find suppliers, which means………….
5.Logistics is the overall management of the way in which all kinds of resources are obtained, stored and moved to the locations ………………
6. One reason large online retailers like Amazon have come to dominate the retail landscape is …………………
a) how resources are handled and moved along the supply chain.
b) where they are required.
c) are acquired, stored, and transported to their final destination.
d) they have to consider logistics.
e) the overall innovation and efficiency of their logistics along every link of the supply chain.
f) as logisticians.
VOCABULARY
Task 1. Match the words in Column A with the correct definitions in Column B.
| A | B |
| 1.carrier | a) a person or a company who provides goods or services to another person or entity. |
| 2. store | b) a company or a person legally entitled to transport goods by land, water, and air. |
| 3. supplier | c) to put or keep things for use in the future. |
| 4. expansion | d) a company or a person that buys products from a manufacturer or wholesaler and sells them to end users or customers. |
| 5. retailer | e) a complete list of items such as property, goods in stock, or the contents of a building. |
| 6. inventory | f) an increase, enlargement, or development in the activities of a company. |
Task 2. Read the Text A again if necessary and find the words which have a similar meaning to the following.
1. convey an idea (paragraph 1)
2. primarily (paragraph 2)
3. go forward (paragraph 2)
4. train in (paragraph 3)
5. productive (paragraph 5)
6. build relationships (paragraph 5)
7. at the present time (paragraph 5)
Task 3. Complete the sentences (1-5) with words from the box.
| overseeing suppliers store collaborates retailers |
1. Logistics Managers act as supervisors by …………… the entire supply chain purchasing and distribution process.
2. A logistics manager …………… with raw material suppliers, merchants, manufacturers, and customers.
3. ……………. typically buy goods from a manufacturer, wholesaler, or other distributor and then resell them to the public.
4. …………… spend millions of dollars on marketing campaigns to help sell products they carry.
5. All businesses must …………. goods and materials safely, especially warehouses, factories, shops, food, agricultural and construction businesses.
LISTENING
Task 1. Watch the video with Ciara Barskietis, a Logistics Manager for Sandvic and then discuss the following questions.
(https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QVpYd831Pes)
1. What does the company produce where Ciara Barskietis works for?
2. What is Ciara Barskietis’ job?
3. What is the responsibility of an export team?
4. Does she enjoy her job? Why?
5. What is her education level?
6. What does she think of the manufacturing industry in Northern Ireland?
Task 2. Match the words in Column A with the words in Column B to make word partnerships. Watch the video again to check your answer.
| A | B |
| 1. warehouse | a) sector |
| 2. aeronautical | b) function |
| 3. manufacturing | c) chain |
| 4. supply | d) engineering |
| 5. finished | e) team |
| 6. export | f) product |
SPEAKING

Work in groups of 3-4 students. Discuss one of these topics in a group. Use phrases from the Useful language box.
Group A: The importance of logistics in business
Group B: The problems in Logistics Industry and solutions.
USEFUL LANGUAGE
Presenting arguments
- It is often said that ……………….., and I cannot disagree with this.
- On the one hand, I would ……………………
- Unfortunately, another point is that if ………………………….
- First of all, there are ……………………………
- The most important point is that ………………………
- On the other hand, I could ………………………..
READING
Task 1. Discuss the following questions before you read the text.
1. Is logistics the same as supply chain management?
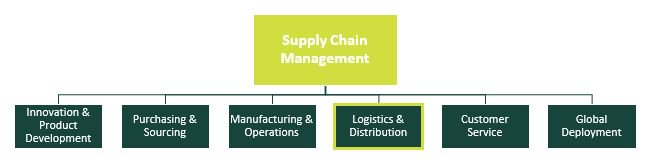
2. How can you explain the meaning of the given table below?
Text B
Task 2. Read the text below and then discuss the following questions.
1. What is supply chain management?
2. What are the three levels of supply chain management?
3. What is the difference between the three levels of supply chain management?
SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT
Supply chain management (SCM) is the management of the flow of goods. It includes the movement and storage of raw materials, work-in-process inventory, and finished goods from point of origin to point of consumption. Interconnected or interlinked networks, channels and node businesses are involved in the provision of products and services required by end customers in a supply chain. Supply chain management has been defined as the "design, planning, execution, control, and monitoring of supply chain activities with the objective of creating net value, building a competitive infrastructure, leveraging worldwide logistics, synchronizing supply with demand and measuring performance globally."
SCM draws heavily from the areas of operations management, logistics, procurement, and information technology, and strives for an integrated approach.
To ensure that the supply chain is operating as efficient as possible and generating the highest level of customer satisfaction at the lowest cost, companies have adopted Supply Chain Management processes and associated technology. Supply Chain Management has three levels of activities that different parts of the company will focus on: strategic; tactical; and operational.
Strategic: At this level, company management will be looking to high level strategic decisions concerning the whole organization, such as the size and location of manufacturing sites, partnerships with suppliers, products to be manufactured and sales markets.
Tactical: Tactical decisions focus on adopting measures that will produce cost benefits such as using industry best practices, developing a purchasing strategy with favored suppliers, working with logistics companies to develop cost effect transportation and developing warehouse strategies to reduce the cost of storing inventory.
Operational: Decisions at this level are made each day in businesses that affect how the products move along the supply chain. Operational decisions involve making schedule changes to production, purchasing agreements with suppliers, taking orders from customers and moving products in the warehouse.
(Adapted from https://www.Introduction to Supply Chain Management |)
Task 3. Are the following statements (1-6) true, false or not given according to the Text B?
1. Supply chain management is the management of the flow of services and goods and has processes that transform raw materials into final products.
2. SCM draws heavily from the area of operations management only and strives for an integrated approach.
3. Supply Chain Management has four levels of activities that different parts of the company will focus on.
4. At the strategic level, company management makes high-level strategic supply chain decisions that are relevant to whole organizations.
5. Tactical-level decisions play an important role in controlling costs.
6. Some of the aspects of operational-level management include daily and weekly forecasting for resource to ensure that enough inventory is available.
Task 4. Match the sentences beginnings (1-7) with the correct endings (a-e) to make a short summary of the Text B. Read the text B again if necessary.
1. Supply chain management has been defined as the "design, planning, execution, control, and ……………………………………………………..
2. To ensure that the supply chain is operating as efficient as possible and generating the highest level of customer satisfaction at the lowest cost, companies ……………………………………………………………….
3. At the strategic level, company management will be looking to high level strategic decisions concerning the whole organization, such as the size and location of manufacturing sites, partnerships with ……………………………
4. Tactical decisions focus on adopting measures that will produce cost benefits such as using industry best practices, developing a purchasing strategy with favored suppliers, working with logistics companies to develop cost effect transportation and ……………………………….
5. Decisions at this level are made each day in businesses that ……………
a) have adopted Supply Chain Management processes and associated technology.
b) developing warehouse strategies to reduce the cost of storing inventory.
c) suppliers, products to be manufactured and sales markets.
d) monitoring of supply chain activities with the objective of creating net value.
e) affect how the products move along the supply chain.
