ВУЗ: Не указан
Категория: Не указан
Дисциплина: Не указана
Добавлен: 14.10.2024
Просмотров: 94
Скачиваний: 0
СОДЕРЖАНИЕ
Word-building. Common prefixes. Common suffixes.
It is useful to know how to build up word families by adding suffixes. Look at these examples:
Word Combinations. Simple Tenses. Everyday English and Technical English.
The neologisms. Continuous Tenses. Computers in our life.
The numeral. Perfect Continuous Tense. The Founder of Microsoft.
To sum up furthermore moreover secondly finally however
2) Give the definition of the terms
Three basic steps of the computer
Interacting with your computer
Lesson 12-14. Computer Memory. Ram. Rom. The Use of Active and Passive Voice.
Modal verbs and their equivalents.
The Power of Programs. Modal Verbs with Passive Infinitive
Lessons 4-5. Software. Application Software
Об'єктний інфінітивний зворот. Складний додаток.
Об'єктний інфінітивний зворот вживається після дієслів:
Суб'єктний інфінітивний зворот
2) Give the definition of the terms
|
data |
keeping data in electronic circuits |
|
data-processing |
the pieces of information that computer processes |
|
storing data |
sorting, adding, rearranging or otherwise manipulating information |
**Task III Translate the sentences into Ukrainian. Practice the use of Participle
1 .The pieces of information processed are called data.
2. Datum meant as something given comes from Latin.
3. When sorting, adding, rearranging information we manipulate it and it’s called data processing.
4. One of the features of computers making them unique is that they store information.
5. The data stored in a computer memory can be recalled, erased or changed.
6 .Being electronic the computer’s memory stores data in electronic circuits.
7. Working together a microprocessor and electronic memory enable the computer the data that it receives.
*Task IV Learn the new vocabulary.
To provide - забезпечувати
Basic - основний
Additional – додатковий
Usable – придатний для використання
To occur – траплятися
Display – зображення
Keyboard – клавіатура
*Task V. Translate the word-combinations given below:
The basic instructions, to provide the instructions, in order to do a specific job, data and additional instructions, to enable to do a specific job, in the form of letters, through a keyboard,
the human brain, a usable form, to do calculations, to display the results, to produce as a result of work, three-step process
*Task VI. Read and translate the text.
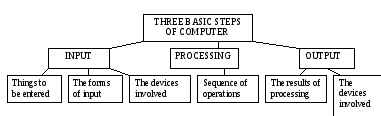
Three basic steps of the computer
INPUT
A program provides the basic instructions so the computer must follow in order to do a specific job. Like the basic rules of a game, the program is only the beginning, however. In order to do a job, the computer and the program must also have input. Input is the data and additional instructions you give to a computer to enable it to do a specific job. The input may be in the form of numbers, letters, words, or pictures The computer may receive input through a keyboard, which looks very much like the keyboard on an ordinary typewriter. It may also receive input from a disk. Until a computer receives input, it can do nothing.
Processing
What does a computer do with the information it receives? Like the human brain, it sorts information, puts it into usable form, and does calculations. This step is called processing.
OUTPUT
Finally, the computer does something with the information it processes. It usually displays the results, often on a screen or on paper. The product of computer processing is called output. Output is the information the computer produces as a result of its work.
You are likely to see this three-step process — input, processing, output — in many day-to-day activities, such as when you use a pocket calculator. In a calculator the input consists of numbers that you press on its keypad — let's say the numbers 3 and 7. The processing occurs after you tell the calculator what you want it to do for example, multiply. The output — 21 — appears on a little screen at the top of the calculator.
The calculator can process the same information in different ways. You might have asked it to add the two numbers, in which case "10" would have appeared on the screen.
**Task VII. Give the English translation to the following:
Основні інструкції до комп’ютера, трьох-ступеневий процес, зображати результати, забезпечувати роботу комп’ютера, схожий на клавіатуру, виконувати обчислення, для того, щоб виконати роботу, отримувати інформацію через клавіатуру, щоденна діяльність, з’явитися на моніторі, складатися з чисел
*Task VIII. Read the following sentences to understand 3-step process of computer and fill in the missing words.
1.A program provides the basic instruction so the computer must … to do a specific job.
2. In order to … the computer and the program must … .
3. The computer may receive input through … or from … .
4. After the inputting the information the computer sorts it, into … and does calculations.
5. Finally the computer … the results often on a … or paper… .
*Task IX. Give the definition oа the major items of the text – input, output, processing. Explain the difference between input and output.
*Task X . Translate the following words into Ukrainian:
To sort – sorting to use – usable available - unavailable
To process – processing to multiply – multiplication result – to result
To calculate –calculation to add – addition able – to enable
**Task XI. Organize the scheme of the 3-steps of the computer to get the main idea of the process:
**Task XII. Answer the questions:
-
What do you need to a specific job on the computer?
-
What is the first step of doing the job?
-
What forms of input do you use?
-
What devices are involved to receive the input?
-
What does a computer do with the information it receives?
-
What is the 3-step process?
-
Name the devices you usually use for the input?
*Task XIII. Read the following sentences, translate them into Ukrainian. Pay your attention to the use of Passive Voice.
1.The basic instructions are provided by computer. 2. The data were given to the computer two minutes ago. 3. The input will be received trough the keyboard. 4. The information is being sorted and put into a usable form now. 5. The calculations were being done when he made records. 6. The results have been already displayed on a screen. 7. He said the output had been displayed on a screen. 8. The work may be done in two seconds.
*Task XIV. State the tense and type of Predicates and translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
1. When the engineer was measuring the temperature he used the ultrasonic technique. When measuring the temperature the engineer used the ultrasonic technique. 2. The temperature the engineer was measuring was of great value for our tests. The temperature was being measured great importance for our tests. 3. When the temperature was being measured it Proved extremely low. Being measured the temperature proved extremely low. 4. When the student had measured the temperature he wrote it down in the table.
**Task XV. Put the Verbs in the brackets in the required forms of the Tense and translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
1. For many years scientists (to study) the nucleus before they found that it is possible to split it. 2. By the first of January our plant (to use) atomic energy for running different machines for eight months. 3. Many power stations (to use) atomic energy for a long time before I knew it. 4. All this period scientists and engineers (to develop) rocket technology and electronics in close cooperation. 5. We widely (to use) electronic devices in industry for many years. 6. We know that our astronomers (to observe) the moon for a long time. 7. My friend (to make) these experiments to compare the weigh of elements since the first of September, 8. The question about the new experiment on this subject (to discuss) for some time before we came to a definite conclusion.
Task XI. State the functions of the words ending-ed and translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
1. Iron and steel are both produced from iron ore. 2. The steel produced by our plant is of high quality. 3. Scientists produced new elements in і nuclear reactors. 4. For very low-temperature work gases are the only substances that can be used. 5. The two very important types of thermometers widely used in industrial processes are electrical in character. 6. We used both types of thermometers in our work. 7. Our laboratory will be provided with all the necessary instruments. 8. The instruments provided by our plant are very accurate. 9. This plant provided a great number of accurate instruments last year. 10. The automatic space station created provides important information on space.
**Parts of a computer
A computer is an electronic machine that accepts, processes, stores and outputs information. A typical computer consists of two parts: hardware and software. Hardware is any electronic or mechanical part of the computer system that you can see or touch.
Software is a set of instructions, called a program, which tells a computer what to do. There are three basic hardware sections.
1 The CPU is the heart of the computer, a microprocessor chip which processes data and coordinates the activities of all the other units.
2 The main memory holds the instructions and data which are being processed by the CPU. It has two main sections: RAM (random access memory) and ROM (read only memory).
3 Peripherals are the physical units attached to the computer. They include: Input devices, which let us enter data and commands (e.g. the keyboard and the mouse).
Output devices, which let us extract the results (e.g. the monitor and the printer).
Storage devices, which are used to store information permanently (e.g. hard disks and DVD-RW drives). Disk drives are used to read and write data on disks. At the back of a computer there are ports into which we can plug external devices (e.g. a scanner, a modem, etc.). They allow communication between the computer and the devices
**Look at A opposite. Read these quotations and say which computer essential they refer to.
1. ‘Accelerate your digital lifestyle by choosing a Pentium at 4.3 GHz.’
2. ‘Right-click to display a context-sensitive menu.’
3. ‘You will see vivid, detailed images on a 17" display.’
4. ‘This will produce high-quality output, with sharp text and impressive graphics.’
5. ‘Use it when you want to let the grandparents watch the new baby sleeping.’
6. ‘Press any key to continue.’
**Match the terms with their definitions.
|
CD/DVD drive Speaker Modem port |
a any socket into which a peripheral device may be connected b device used to produce voice output and play back music c mechanism that reads and/or writes to optical discs d device that converts data so that it can travel over the Internet |
**Complete the diagram and sentences below with words from C opposite.

1 Computer is the visible or audible result of data processing – information that can be read, printed or heard by the user.
2 The CPU will process data as instructed by the programs you're running includes functions like calculating, sorting, editing, drawing and searching.
3 DVDs are expected to replace CDs as devices.
4 As a scanner, the Sigma-100 can be used to photographs as well as documents into the computer.
Interacting with your computer
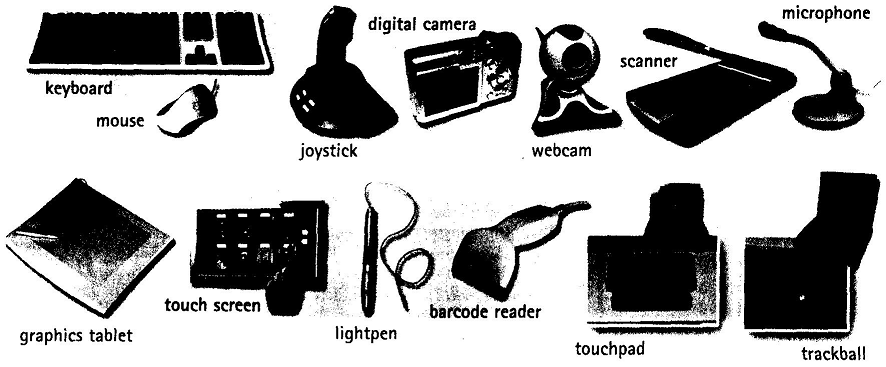
Input devices are the pieces of hardware which allow us to enter information into the computer.
A standard PC keyboard has various groups of keys.
-
Alphanumeric keys - these represent letters and numbers, arranged as on a typewriter.
-
A numeric keypad appears to the right of the main keyboard and contains numeric and editing keys; the Num Lock key is used to switch from numbers to editing functions.
-
Function keys appear at the top of the keyboard and can be programmed to do special jobs.
-
Cursor keys include 'arrow keys' which move the insertion point, and keys such as Home, End, Page Up, and Page Down, which let you move around documents.
-
Dedicated keys are used to issue commands or produce alternative characters. For example: Ctrl changes the functions of other keys (e.g. Ctrl + X cuts the selected text).
Caps Lock sets the keyboard in 'CAPITALS' mode; it only affects letters.
Enter (or Return) is pressed to select options from a menu or to start a new paragraph.
Backspace deletes the character to the left of your current position.
The mouse
A mouse is a hand-held device that lets you move a pointer (or cursor) and select items on the screen. It has one or more buttons to communicate with the PC. A scroll wheel lets you move through your documents or web pages The pointer looks like an I-bar, an arrow or a pointing hand.
An optical mouse has an optical sensor instead of a ball underneath. A cordless (wireless) mouse has no cable; it sends data via infrared signals or radio waves. Mouse actions:
-
to click, press and release the left button.
-
to double-click, press and release the left button twice.
-
to drag, hold down the button, move the pointer to a new place and then release the button.
-
to right-click, press and release the right button; this action displays a list of commands.
Voice input
Today you can also interact with your computer by voice with a voice-recognition system that converts voice into text, so you can dictate text directly onto your word processor or email program. You can also control your PC with voice commands; this means you can launch programs, open, save or print files. Some systems let you search the Web or chat using your voice instead of the keyboard.
to copy images from paper into a computer
to read price labels in a shop
to select text and click on links on web pages
to enter drawings and sketches into a computer
to input voice commands and dictate text 1 to draw pictures or select menu options directly on the screen 8 to take and store pictures and then download them to a computer.
**Complete each sentence by choosing from the following devices: touch screen, trackball, touchpad, webcam.
1 A is a stationary device that works like a mouse turned upside down. You roll the ball with your hand to move the pointer on the screen.
2 Interactive are used in museums, information centres and Internet kiosks. You use your finger to point directly to objects on the screen.
3 ……………. is used to send live video images via the Internet.
4 A……………… is found on notebook PCs. You use it by pressing the sensitive pad with a finger.
** Label the groups of keys with terms from B opposite. Then identify the keys described below.
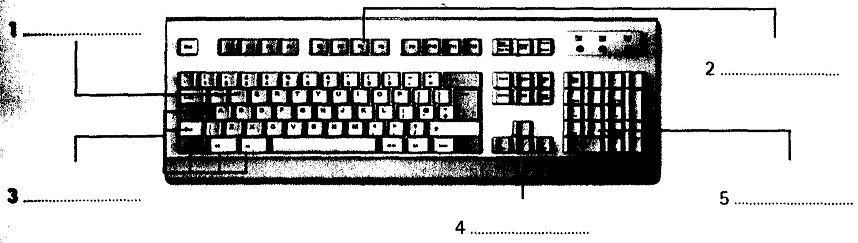
6 It produces upper-case letters, but it does not affect numbers and symbols.
7 It removes the character to the left of the cursor or any selected text.
8 It works in combination with other keys, e.g. you press this key and C to copy the selected text.
9 It is used to confirm commands; in a word processor, it creates a new paragraph.
**Look at C opposite. Complete these sentences with the correct 'mouse action'.
1 To start a program or open a document you ………….. on its icon - that is, you rapidly press and release the mouse button twice.
2 If you want to select a menu option, you just…………… on the left button.
3 If you want to find the commands for a particular text, image, etc., you have to ……………… on it.
4 If you want to move an object, press the button and ……………… the object to the desired location.

